The following page describes how customer-specific comparison logics can be implemented.
Programming example
In this example, the tests of 2 different qualities are to be compared.
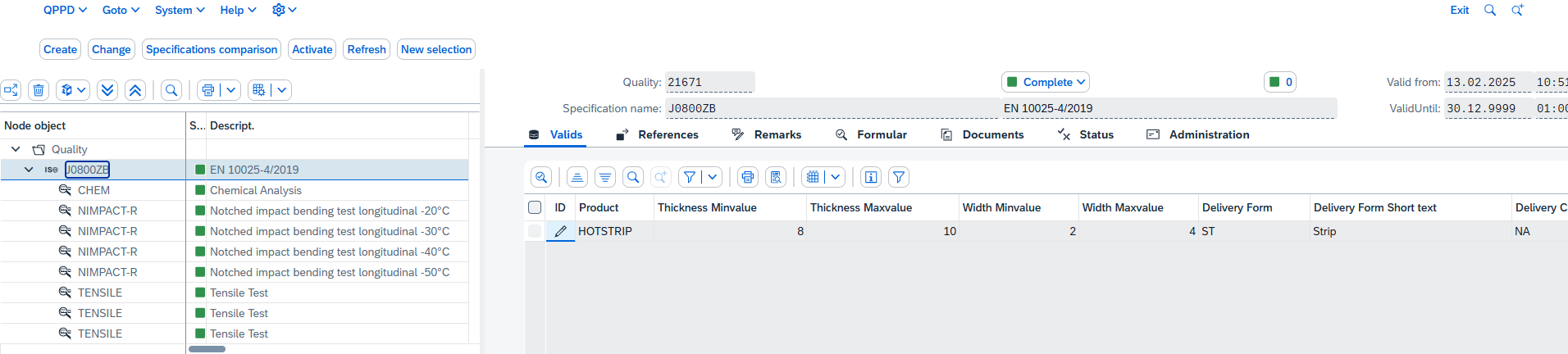
Description of the object QUALITY
The object is of specification type QUALITY, which in this case describes various tests for materials. These tests, such as chemical analysis, notched impact bending test and tensile test, are all of item type TESTING. Each of these subordinate test nodes contains specific target values and test parameters that are relevant for quality assurance.
A quality can have several nodes of type TESTING. Each of these nodes has a condition object type assigned to it. The condition object type determines the conditions under which the target values are defined. The target values define the expected properties of a test. For example, they specify which chemical composition a material must have or which minimum and maximum values apply to tests.
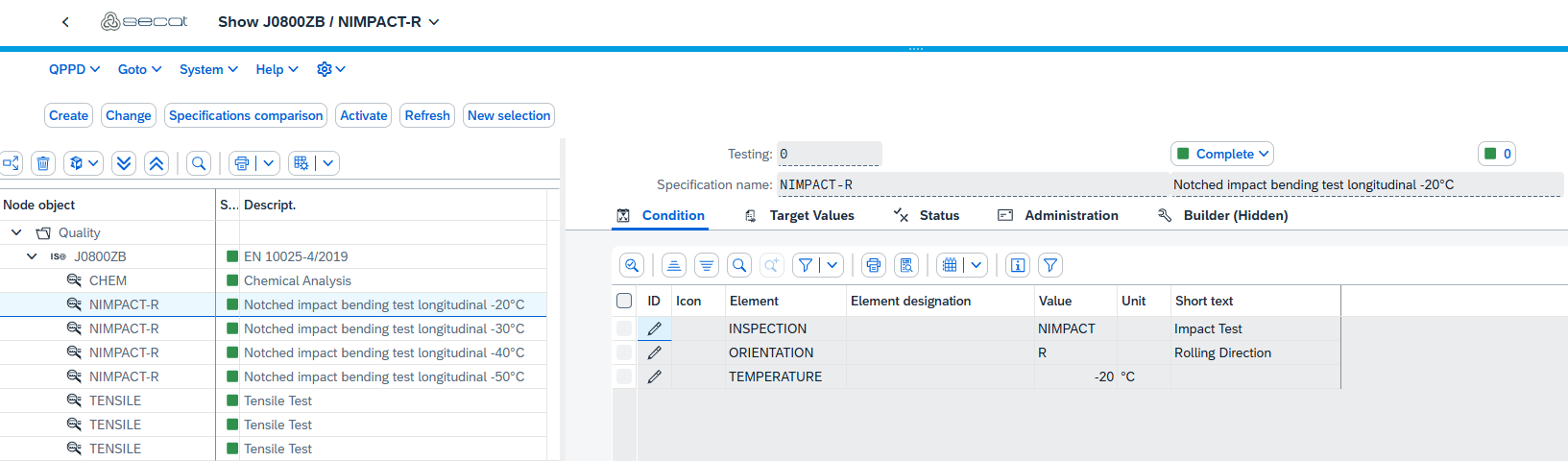
Each condition object type has various elements that describe the test context in more detail. The INSPECTION element specifies the type of test. The ORIENTATION element describes the sample location. The TEMPERATURE element plays a role in mechanical tests, as the material behavior changes with temperature. If these parameters deviate, the target values may change.
The combination of item type and condition object type makes it possible to manage and evaluate different types of tests in a structured manner. This means that several test nodes of the same type and different conditions can exist in the quality.
Technically, it is possible to compare all tests directly with each other, as they are all managed under the higher-level quality object and have the same item category. From a technical point of view, however, this makes little sense, as a chemical analysis, for example, cannot be directly compared with a tensile test. This is where the comparison logic comes into play. It ensures that only meaningful comparisons are made by checking whether two nodes belong together in terms of content. This prevents test values from being compared with each other without a technical connection.
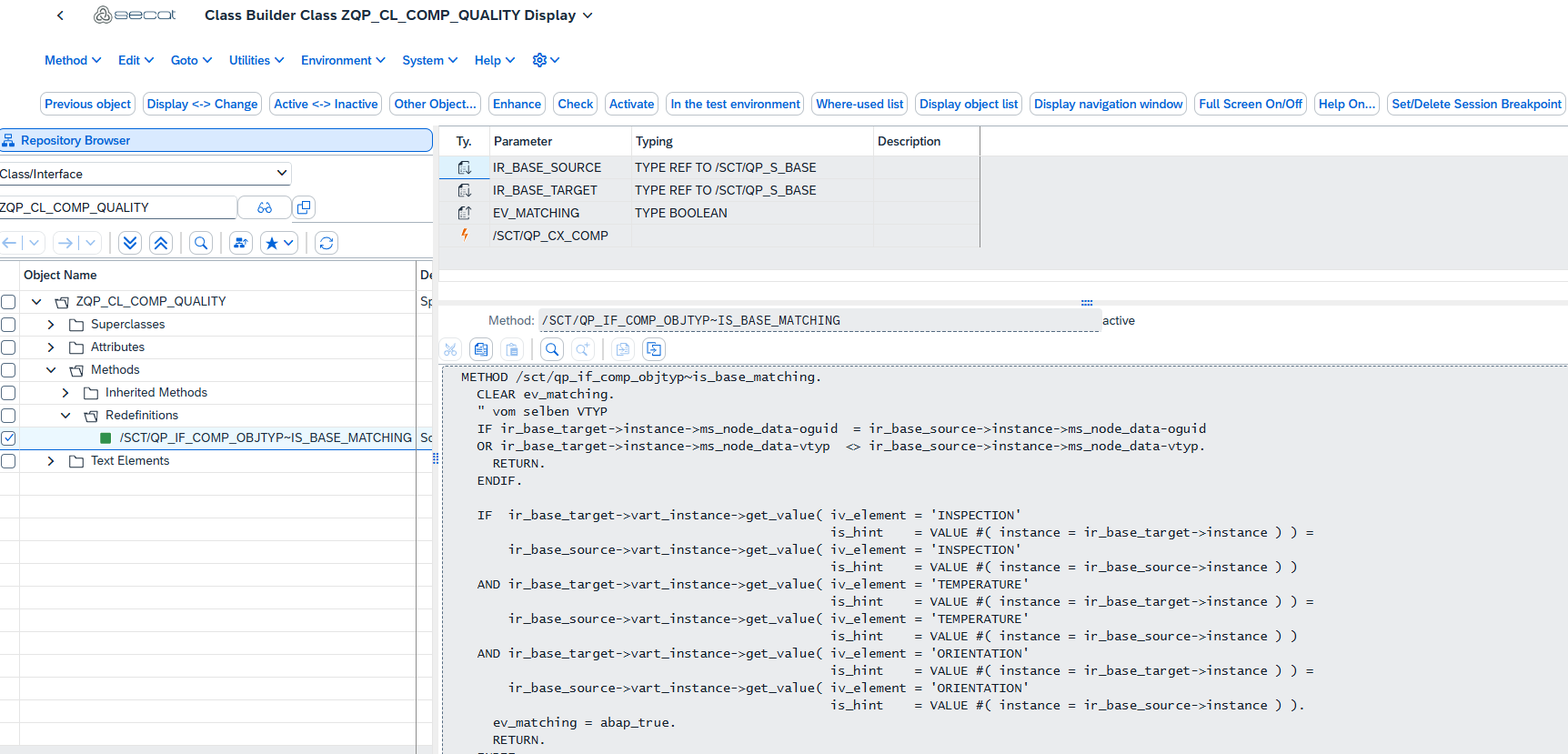
This logic must be implemented in the /SCT/QP_IF_COMP_OBJTYP~IS_BASE_MATCHING method. As only the tests of two different qualities are to be compared, in our case it is first checked whether they have the same OGUID or different item types. If one of these applies, the method is terminated without a hit. The INSPECTION, TEMPERATURE and ORIENTATION elements are also compared. If the values match, objects were found that are comparable. The objects are then displayed and compared in the specifications comparison.
This logic enables a targeted comparison of relevant objects and can be expanded to include additional comparison criteria if required.
A new class must be created in the customer namespace.
The class must inherit from class /SCT/QP_CL_COMP_OBJTYP.
The method /SCT/QP_IF_COMP_OBJTYP~IS_BASE_MATCHING is the only method that should be redefined by the customer.
This class must be added in Customizing under Comparison objects.
The following code can be used to fulfill the above requirements.
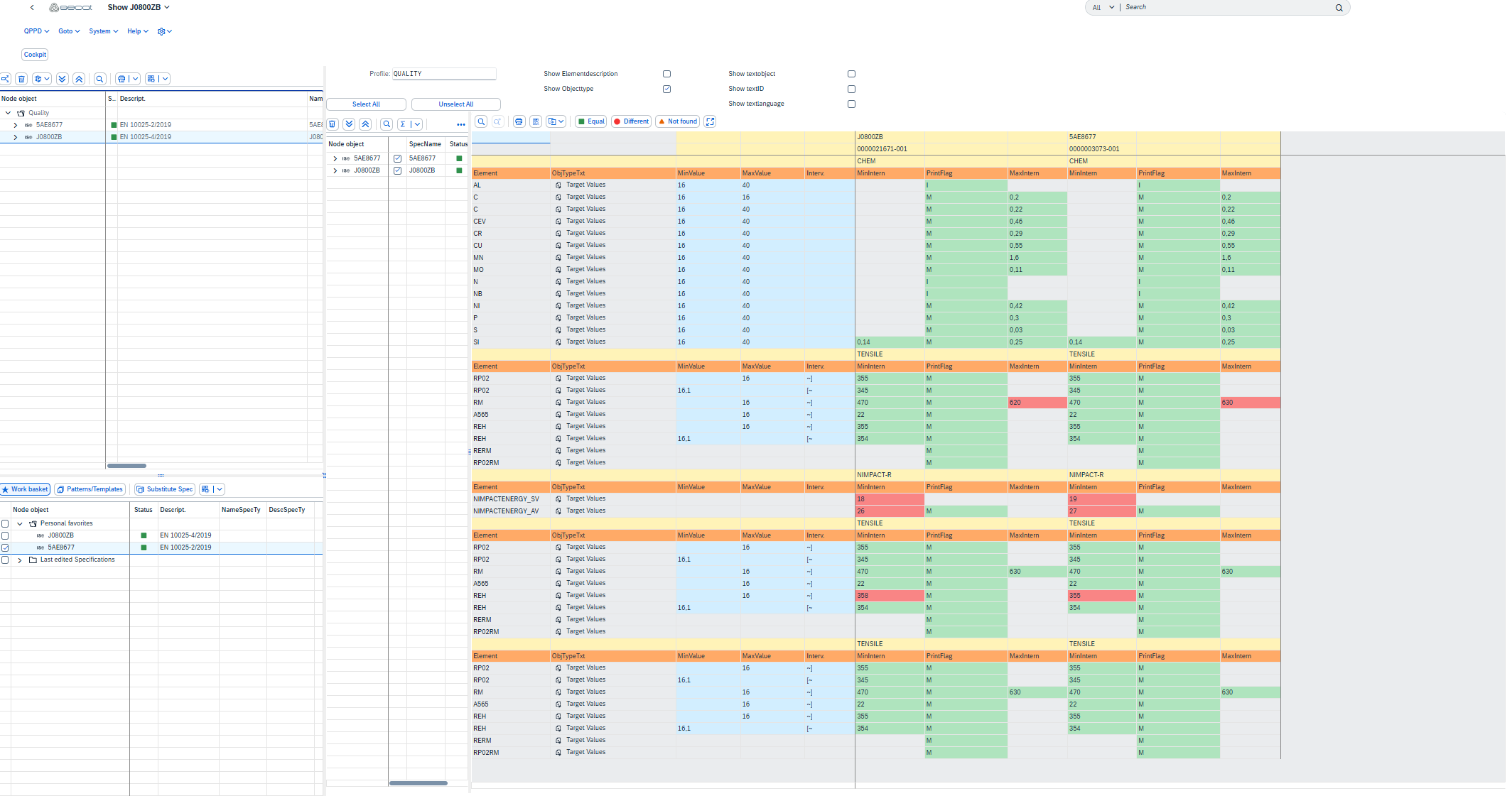
This is what the specifications comparison from the example looks like: