This chapter describes the necessary settings in QPPD customizing so that standard QPPD objects can be distributed between two systems using RFC.
The RFC service uses the IDOC distribution model, but objects are distributed using RFC rather than IDOC.
Settings in QPPD Customizing
Follow-up processes (C25/C30)
The distribution of objects using RFC is based on the distribution model and can be customized at the level of the specification type and the item type.
In the following, the customizing for the distribution via RFC is illustrated using the specification type DOMAIN. Customizing can also be set for item types in the same way.
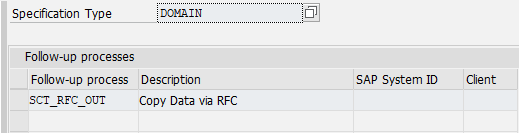
So that an object can be distributed by RFC, the standard follow-up process SCT_RFC_OUT must be assigned to the object. Optionally, a system and/or client can be assigned to the follow-up process. If a system or client is assigned, the distribution takes place, utilizing RFC, for the respective system and/or client. If, as shown in the figure, no system or client is assigned to the follow-up process, the distribution will be made by RFC for this object for all systems and clients.
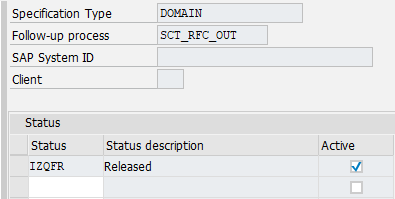
In this example, the distribution for the object, utilizing RFC, only takes place in the status Released. Therefore, a corresponding entry is created in the Status subdialog. The following image shows this entry:
If required, additional statuses can be added to the object, for which the distribution is to take place via RFC. If no status is set, the distribution takes place via RFC for each status.
Advantages of distributing objects via RFC compared to data distribution via IDOC:
Partner profiles are not required
No input/output processing is required
Disadvantages of distributing objects using RFC compared to distributing data using IDOC:
It is not per se possible to trace when a distribution has taken place.