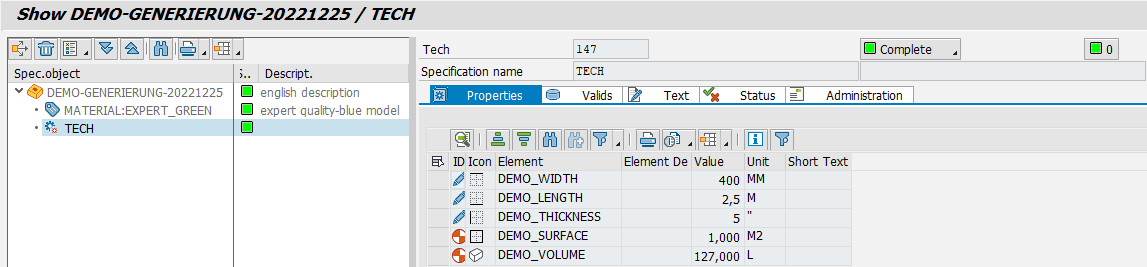
This example is based on the PROPERTIES tab of the DEMO_TECH node under the DEMO_BASIC rule type.
Suppose a cuboid is described (A cuboid is a geometric solid bounded by 6 rectangles).
5 elements are available on the tab:
3 of them are set manually by the user:
The width of the object: demo_width
The length of the object: demo_length
The height (thickness) of the object: demo_thickness
2 can be calculated automatically ( for this purpose 2 generation methods are used which build on each other )
The area of the object: demo_surface
Area = Width x LengthThe volume of the object: demo_volume
volume = Surface x height
The 3 classes mentioned below are functionally identical:
The area and volume of the object are calculated taking into account the units entered, but the technical implementation is different.
Scenario 1: Transfer with individual parameters
Class: /SCT/ZQP_CL_GEN_TECH_SINGLE
The naming of the methods does not matter: based on the analysis of the import and export parameters, the method for determining the area is called first, then the method for determining the volume.
Advantages:
Easy access
Automatic sequence
Disadvantages:
Cluttered if many elements are required on the tab
Cannot be used if there are multiple elements on the tab page
Scenario 2: Transfer with parameter table
Class: /SCT/ZQP_CL_GEN_TECH_TAB
Advantages:
Simple Signature
Suitable for the multiple evaluation of elements
All evaluated elements are automatically made available as an import.
Disadvantages:
No automatic sequence
With a large number of elements, the preparation of all import parameters can be time-consuming.
"Manual" preparation of export parameters necessary
Scenario 3: Without import parameters
Class: /SCT/ZQP_CL_GEN_TECH_NOIMPORT
Advantages:
The developer selects the most appropriate access method for the import parameters
Disadvantages:
No automatic sequence
"Manual" preparation of export parameters necessary